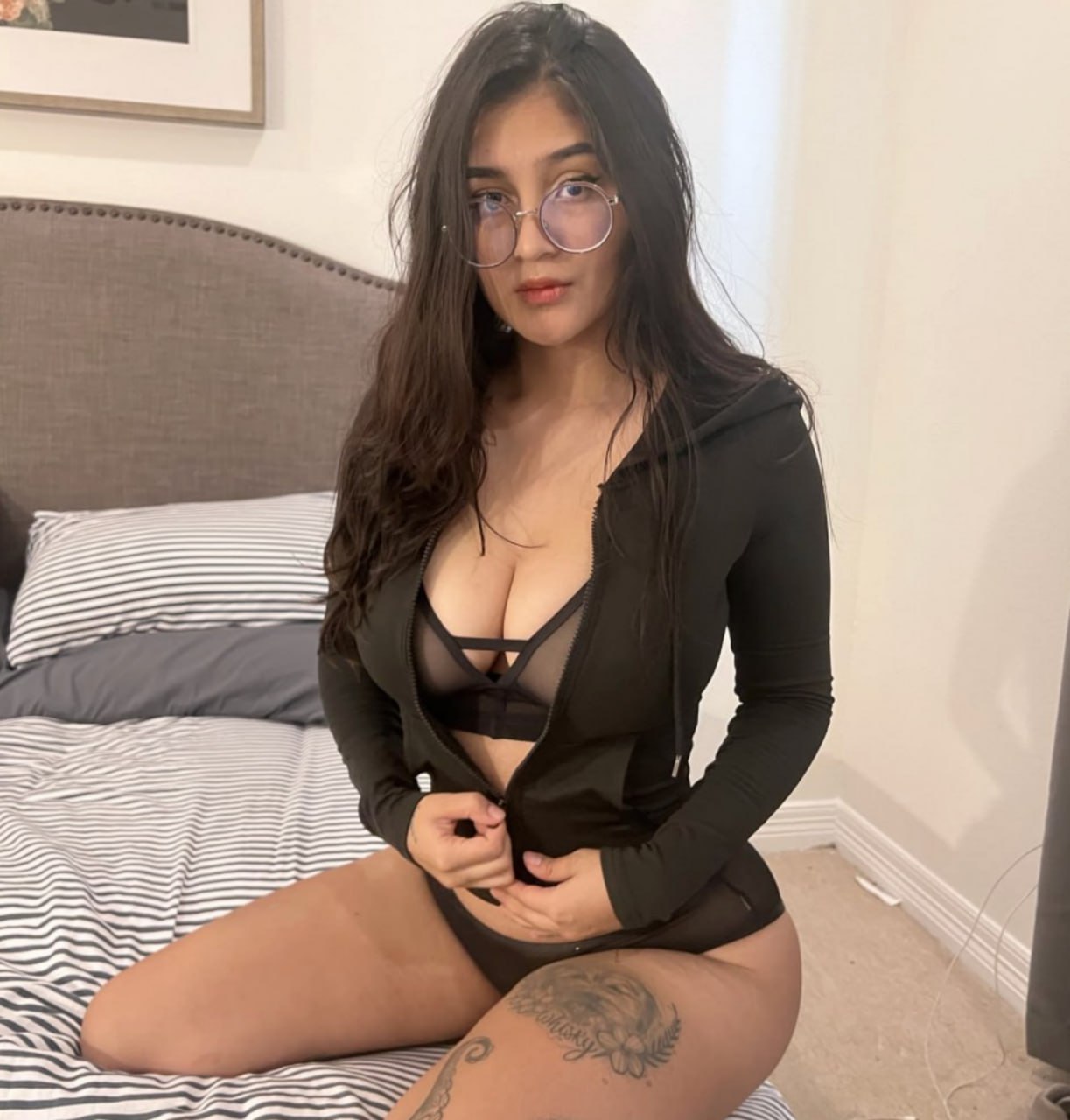
H&B givemeahand OnlyFans Profile - Free Posts, Photos, Videos, Nudes, Leaked
@givemeahand's Biography
Hi wonderer 👀!
So, first of all, I am not a customer of this app 😅
My account will for now post information about one of the most complex, intriguing and oldest engine : the human body 🧠.
As to know why I was doing this with pics of my hands 🤲 ... Let's just say I find them weird and funny I guess 🖖.
Feel free to come talk to me in my dms 💬, I might or might not answer. It will depend of my mood and availability 💆.
Love
@givemeahand's Latest Posts, Photos and Videos
VEINS
With the exception of the pulmonary vein, that is connecting the lungs to the hearth, the veins are blo od vessels transporting the deoxygenated blo od from the tissues to the heart. They are more veins than arteries.
Veins also have 3 layers: internal, medium and external, made of elastic, connective and muscular elements. Many veins have valves that prevent the blo od reflux. The medium layer contract and dilate the vein to control the body temperature.
The superficial veins carry the blo od just under the skin. When the body temperature is too high, they are dilating to eliminate some heat. To keep the heat, veins are contracting, making the skin pale.
Even though they are visible through the skin as thin blue lines, the blo od that they are carrying is indeed dark red. This darker color is due to the haemoglobin present into the blo od, connecting more easily to the carbon dioxide rather than the oxygen.
As well as 75% of carbon dioxide is dissolved into the blo od plasma, the venous blo od is more acid than the arterial blo od.
ARTERIES
SUMMARY
- Arteries carry oxygenated blo od to the heart with one exception: the pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blo od.
There are big and medium caliber arteries, as well as arterioles, that immediately preceed the capillaries.
An artery has 3 layers: an external one, made of connective tissues and elastic fibers, a middle one also made of elastic fibers and muscular fibers, and an inner one made of endothelial cells surrounded by lengthwise elastic fibers and connective tissues.
Arteries are usually located deep into the body to avoid common injuries. The arterial blo od oxygen high rate gives it its red color, brighter than the one from the veins. If the blo od coming from an injury is bright red, it means that an artery is damaged.
The muscular fibers of those walls contract and dilate the artery to help it regulate its internal blo od pressure, that is going up and down to the rhythm of the heartbeats.
HAPPY NEW YEAR EVERYONE! ENJOY YOUR TIME WHEREVER YOU MIGHT BE
THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
SUMMARY
A circulatory system is a system made of organs in circuit allowing fluids to circulate in an organism.
The cardiovascular system has a double circular structure, meaning that it has two vessels loops starting from the heart. Each loop is made of 3 vessel types: the arteries that carry the blo od far from the heart, the veins that carry it back to the heart and tiny capillaries that are going through the tissues.
The overall circulation, the bigger loop, that gives the oxygen to the whole body except the lungs, is starting from the aorta, the main artery, 2 centimeters large. The aorta appears from the left ventricle and loops in the abdomen, giving birth to all the arteries.
The overall circulation is bringing back the blo od to the heart, and more precisely into the left atrium through 2 big veins, the upper and lower vena cava. The pulmonary artery carries the deoxygenated blo od brought by the vena cave from the right ventricle all the way to the lungs.
The pulmonary vein escorts back the blo od filled with oxygen to the left atrium, where it goes back to the general circulation.
THE CARDIAC CONDUCTION
SUMMARY
- The cardiac conduction is a 5 steps cardiac cycle of contractions and releases.
The cardiac conduction is characterized by a bitonal sound, caused by a series of contractions through the hearth going from top to bottom, contracting the atriums just before the ventricles.
The cycle is initiated by the sino-atrial node, located in the right atrium wall, that generates an electric stimulus transmitted to the cardiac muscle. The frequency of the cardiac cycle (heart rate) is influenced by the nerve pulsions send by the brain to the spinal cord.
At the first cycle step, the heart is relaxed, and the atrio-ventricular valves are opening. At the second step, the atriums are contracting, pushing the blo od into the ventricles. The atrio-ventricular valves are closing and the ventricles are starting to compress the blo od to the third step.
At the fourth step, the semi-lunar valves (aortic and pulmonary), located at the exits close to the ventricles, are opening. During the last step, the semi-lunar valves are closing to prevent the blo od to come backwards, and the emptied ventricles are starting to relax.
THE HEART
SUMMARY
- The heart is a pyramidal shaped organ located in the thoracic cavity. It is the main element of the blo od circulation.
It weights approximately 300 grams and is divided into 4 cavities, each is surrounded with a thick muscular wall. The cardiac muscle can strongly contract itself without getting tired, unlike the bone muscles.
The 2 superior intern cavities are the atriums, the 2 lower ones, much larger, are the ventricles. The blo od arrives into the heart by the atriums and leaves by the ventricles.
The heart is usually studied by side. The left side is getting the oxygenated blo od from the lungs and is pumping it to the rest of the body. The right side is getting the deoxygenated blo od from the body and is sending it to the lungs to be refilled in oxygen.
The left cavities are larger and more muscular because they have more work to do. The entry and exit points of the 2 ventricles have valves that are closing to allow the rise of blo od pressure, so that the heart can push it into the blo od vessels.
BONE MARROW
SUMMARY
- The bone marrow is of 2 types, yellow and red, and is responsible for the hemapoiesis.
Every blo od corpuscle is essentially produced in the red bone marrow from short and flat bones (sternum, ribs, vertebreas, coxal bones).
The production of red blo od cells is stimulated by the erythropoietin hormone produced itself by the kidneys when the volume of oxygen in the blo od is suspected to be low (indicates that their number needs to be higher).
The red blo od cells are made from a hemocytoblast, a germ cell capable of producing every blo od corpuscle type, that are dividing multiple times and specializing after each division. While in the proerythroblast stage, the cell is starting to increase its haemoglobin rate.
When reaching the next stage, the erythroblast, the core is expelled. At the final stage, the erythrocytes are forming. The yellow bone marrow is filling the diaphysis medullary cavity of long bones.
Their epiphysis are made of spongy bone tissues and red bone marrow. The arteries and veins that are going through those bones are injecting blo od corpuscles made by the red bone marrow into the blo od.
Each cube milliliter of blo od has around 5 millions of red blo od cells in general, also called erythrocytes. Red blo od cells contain haemoglobin, that carries the oxygen inside the tissues. The color pink-red is caused by the presence of iron in the haemoglobin molecules.
The red blo od cells have no cellular core and 96% of their dry weight comes from the haemoglobin. Each haemoglobin molecule can simultaneously transport 4 oxygen molecules. By realizing this oxygen, the haemoglobin is taking car of some carbon dioxide which it carries back to the lungs.
However, most of the wastes are dissolved into the blo od plasma. Usually, a red blo od cell is circulating for a 100 days before being eliminated by the liver.
BLO OD
SUMMARY
- Blo od is a thick red biological liquid, composed of plasma and cellular elements and including almost a hundred of chemical substances in solution or in suspension. It is circulating in the cardiovascular system.
Those cellular elements are the leukocytes (white blo od cells), the erythrocytes (red blo od cells) and the thrombocytes (blo od platelets).
When the blo od is divided into a centrifuge, its heavier components (blo od corpuscles) are going downward in the sample, while the lighter ones (plasma) are going upward. Between the two, a small white ring contains the leukocytes and the platelets, representing less th an 1% of the blo od total volume.
The platelets are involved in the blo od coagulation. The cellular elements are 45% of the total volume. The 55% left is the blo od plasma, a yellow liquid made at 92% of water, the other 8% being proteins, especially the serum albumine that thicken the blo od and raise its superficial tension, ensuring that its stays homogeneous while circulating.
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
SUMMARY
- The cardiovascular system is a closed-circuit circulatory system that ensures the blo od transport from the heart to the body extremities and divers organs.
Including the heart and the blo od vessels, the cardiovascular system is the main transport system of the body, conveying 5 litters of blo od. The cardiac pump is constantly disseminating the blo od into the blo od vessels and the heart. A full circuit around the body takes approximately a minute.
The blo od vessels also connect the main body glands and send the hormones and the diver chemical signals produced by them.
The intestinal nutrients are going into the body through the blo od. The most vital role (or the most constant one at least) of the cardiovascular system is the collected oxygen transport, collected from the lungs, to every and each body cell.
The blo od vessels, hollow ducts, but differently structured depending on where the blo od it is transporting is going and what its composition is. They are of 3 types : artery, vein and capillaries. The blo od has multiple roles. It is composed of immune system elements, ready to attack infections.
HICCUPS
SUMMARY
- Hiccup is an unwanted physiological reflex characterized by a succession of inhaling spasmodic contractions.
Inhaling and exhaling, but also sneezing, couching and laughing, are following a specific sequence of phases.
When those phases are not synchronized, we end up with the hiccup, an involuntary spasmodic contraction of the diaphragm, that leads to a brusque tremor of the abdomen and the thorax, and is followed by a characteristic hoarse noise, caused by the epiglottis constriction.
The epiglottis and the glottis (the space between the vocal cords) are supposed to be wild open to allow the air arrival. However, if they are closed during the inhaling, the last air portion to go through the vocal cords cause a hiccup.
The reason behind hiccup is not well-known. It could be linked to the fact that the stomach is full: the hiccup seems to be the body's way to cause a pressure drop, that will make trapped air bubbles from the stomach to go upward in the œsophagus.
It is also said that hiccups are an element from the fœtal development of the diaphragm nervous control kept at the adult age.

Unlock a world of visual delight of givemeahand. The onlyfans account has 52 photos and 0 videos.
All posts got more than 3 likes.
No strings attached, no hidden fees – just 52 pieces of captivating content waiting for you.
Join onlyfans community today and embark on a journey of inspiration and creativity, all on the house!
You can also send them a photo or video message for free.



































